The Geography of Puerto Rico
The Geography of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rican Geography
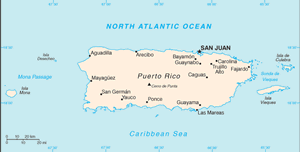
Location: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, east of the Dominican Republic
Geographic coordinates: 18 15 N, 66 30 W
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area: total: 13,790 sq km land: 8,870 sq km water: 4,921 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly less than three times the size of Rhode Island
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 501 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: tropical marine, mild; little seasonal temperature variation
Terrain: mostly mountains with coastal plain belt in north; mountains precipitous to sea on west coast; sandy beaches along most coastal areas
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Caribbean Sea 0 m highest point: Cerro de Punta 1,339 m
Natural resources: some copper and nickel; potential for onshore and offshore oil
Land use: arable land: 3.69% permanent crops: 5.59% other: 90.72% (2005)
Irrigated land: 400 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: periodic droughts; hurricanes
Environment - current issues: erosion; occasional drought causing water shortages
Environment - international agreements:
Geography - note: important location along the Mona Passage - a key shipping lane to the Panama Canal; San Juan is one of the biggest and best natural harbors in the Caribbean; many small rivers and high central mountains ensure land is well watered; south coast relatively dry; fertile coastal plain belt in north