The Geography of Eritrea
The Geography of Eritrea
Eritrean Geography
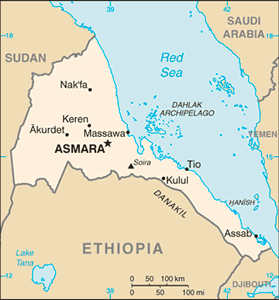
Location: Eastern Africa, bordering the Red Sea, between Djibouti and Sudan
Geographic coordinates: 15 00 N, 39 00 E
Map references: Africa
Area: total: 121,320 sq km land: 121,320 sq km water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Pennsylvania
Land boundaries: total: 1,626 km border countries: Djibouti 109 km, Ethiopia 912 km, Sudan 605 km
Coastline: 2,234 km (mainland on Red Sea 1,151 km, islands in Red Sea 1,083 km)
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm
Climate: hot, dry desert strip along Red Sea coast; cooler and wetter in the central highlands (up to 61 cm of rainfall annually, heaviest June to September); semiarid in western hills and lowlands
Terrain: dominated by extension of Ethiopian north-south trending highlands, descending on the east to a coastal desert plain, on the northwest to hilly terrain and on the southwest to flat-to-rolling plains
Elevation extremes: lowest point: near Kulul within the Danakil depression -75 m highest point: Soira 3,018 m
Natural resources: gold, potash, zinc, copper, salt, possibly oil and natural gas, fish
Land use: arable land: 4.78% permanent crops: 0.03% other: 95.19% (2005)
Irrigated land: 210 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: frequent droughts; locust swarms
Environment - current issues: deforestation; desertification; soil erosion; overgrazing; loss of infrastructure from civil warfare
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: strategic geopolitical position along world's busiest shipping lanes; Eritrea retained the entire coastline of Ethiopia along the Red Sea upon de jure independence from Ethiopia on 24 May 1993