The Geography of Bhutan
The Geography of Bhutan
Bhutanese Geography
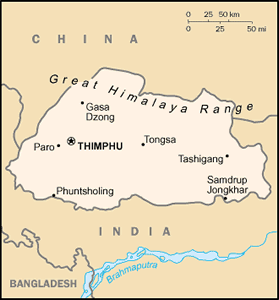
Location: Southern Asia, between China and India
Geographic coordinates: 27 30 N, 90 30 E
Map references: Asia
Area: total: 47,000 sq km land: 47,000 sq km water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative: about one-half the size of Indiana
Land boundaries: total: 1,075 km border countries: China 470 km, India 605 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Climate: varies; tropical in southern plains; cool winters and hot summers in central valleys; severe winters and cool summers in Himalayas
Terrain: mostly mountainous with some fertile valleys and savanna
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Drangme Chhu 97 m highest point: Kula Kangri 7,553 m
Natural resources: timber, hydropower, gypsum, calcium carbonate
Land use: arable land: 2.3% permanent crops: 0.43% other: 97.27% (2005)
Irrigated land: 400 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: violent storms from the Himalayas are the source of the country's name, which translates as Land of the Thunder Dragon; frequent landslides during the rainy season
Environment - current issues: soil erosion; limited access to potable water
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
Geography - note: landlocked; strategic location between China and India; controls several key Himalayan mountain passes