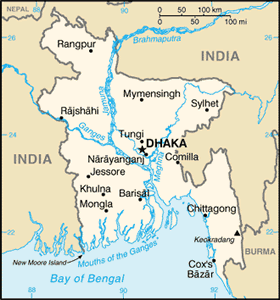
The Geography of Bangladesh
The Geography of Bangladesh
Bangladeshi Geography
Location: Southern Asia, bordering the Bay of Bengal, between Burma and India
Geographic coordinates: 24 00 N, 90 00 E
Map references: Asia
Area: total: 144,000 sq km land: 133,910 sq km water: 10,090 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Iowa
Land boundaries: total: 4,246 km border countries: Burma 193 km, India 4,053 km
Coastline: 580 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm contiguous zone: 18 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm continental shelf: up to the outer limits of the continental margin
Climate: tropical; mild winter (October to March); hot, humid summer (March to June); humid, warm rainy monsoon (June to October)
Terrain: mostly flat alluvial plain; hilly in southeast
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m highest point: Keokradong 1,230 m
Natural resources: natural gas, arable land, timber, coal
Land use: arable land: 55.39% permanent crops: 3.08% other: 41.53% (2005)
Irrigated land: 47,250 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: droughts; cyclones; much of the country routinely inundated during the summer monsoon season
Environment - current issues: many people are landless and forced to live on and cultivate flood-prone land; waterborne diseases prevalent in surface water; water pollution, especially of fishing areas, results from the use of commercial pesticides; ground water contaminated by naturally occurring arsenic; intermittent water shortages because of falling water tables in the northern and central parts of the country; soil degradation and erosion; deforestation; severe overpopulation
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: most of the country is situated on deltas of large rivers flowing from the Himalayas: the Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna to eventually empty into the Bay of Bengal