The Geography of Bahamas, The
The Geography of Bahamas, The
Bahamian Geography
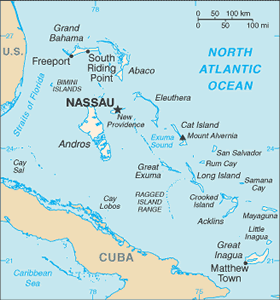
Location: Caribbean, chain of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Florida, northeast of Cuba
Geographic coordinates: 24 15 N, 76 00 W
Map references: Central America and the Caribbean
Area: total: 13,940 sq km land: 10,070 sq km water: 3,870 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Connecticut
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 3,542 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: tropical marine; moderated by warm waters of Gulf Stream
Terrain: long, flat coral formations with some low rounded hills
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m highest point: Mount Alvernia, on Cat Island 63 m
Natural resources: salt, aragonite, timber, arable land
Land use: arable land: 0.58% permanent crops: 0.29% other: 99.13% (2005)
Irrigated land: 10 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: hurricanes and other tropical storms cause extensive flood and wind damage
Environment - current issues: coral reef decay; solid waste disposal
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: strategic location adjacent to US and Cuba; extensive island chain of which 30 are inhabited