The Geography of Suriname
The Geography of Suriname
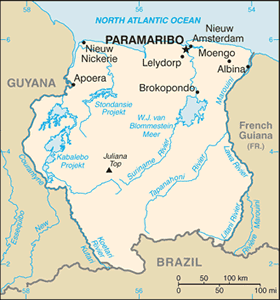
Surinamese Geography
Location: Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana
Geographic coordinates: 4 00 N, 56 00 W
Map references: South America
Area: total: 163,270 sq km land: 161,470 sq km water: 1,800 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Georgia
Land boundaries: total: 1,703 km border countries: Brazil 593 km, French Guiana 510 km, Guyana 600 km
Coastline: 386 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: tropical; moderated by trade winds
Terrain: mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps
Elevation extremes: lowest point: unnamed location in the coastal plain -2 m highest point: Juliana Top 1,230 m
Natural resources: timber, hydropower, fish, kaolin, shrimp, bauxite, gold, and small amounts of nickel, copper, platinum, iron ore
Land use: arable land: 0.36% permanent crops: 0.06% other: 99.58% (2005)
Irrigated land: 510 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: NA
Environment - current issues: deforestation as timber is cut for export; pollution of inland waterways by small-scale mining activities
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: smallest independent country on South American continent; mostly tropical rain forest; great diversity of flora and fauna that, for the most part, is increasingly threatened by new development; relatively small population, mostly along the coast