The Geography of Rwanda
The Geography of Rwanda
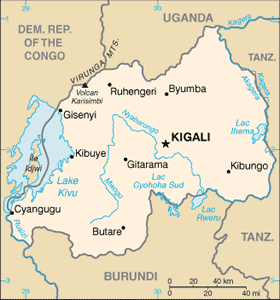
Rwandan Geography
Location: Central Africa, east of Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates: 2 00 S, 30 00 E
Map references: Africa
Area: total: 26,338 sq km land: 24,948 sq km water: 1,390 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Maryland
Land boundaries: total: 893 km border countries: Burundi 290 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 217 km, Tanzania 217 km, Uganda 169 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Climate: temperate; two rainy seasons (February to April, November to January); mild in mountains with frost and snow possible
Terrain: mostly grassy uplands and hills; relief is mountainous with altitude declining from west to east
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Rusizi River 950 m highest point: Volcan Karisimbi 4,519 m
Natural resources: gold, cassiterite (tin ore), wolframite (tungsten ore), methane, hydropower, arable land
Land use: arable land: 45.56% permanent crops: 10.25% other: 44.19% (2005)
Irrigated land: 90 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: periodic droughts; the volcanic Virunga mountains are in the northwest along the border with Democratic Republic of the Congo
Environment - current issues: deforestation results from uncontrolled cutting of trees for fuel; overgrazing; soil exhaustion; soil erosion; widespread poaching
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea
Geography - note: landlocked; most of the country is savanna grassland with the population predominantly rural