The Geography of Jordan
The Geography of Jordan
Jordanian Geography
Location: Middle East, northwest of Saudi Arabia
Geographic coordinates: 31 00 N, 36 00 E
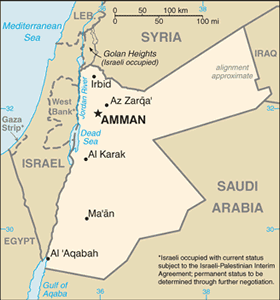
Map references: Middle East
Area: total: 92,300 sq km land: 91,971 sq km water: 329 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Indiana
Land boundaries: total: 1,635 km border countries: Iraq 181 km, Israel 238 km, Saudi Arabia 744 km, Syria 375 km, West Bank 97 km
Coastline: 26 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 3 nm
Climate: mostly arid desert; rainy season in west (November to April)
Terrain: mostly desert plateau in east, highland area in west; Great Rift Valley separates East and West Banks of the Jordan River
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Dead Sea -408 m highest point: Jabal Ram 1,734 m
Natural resources: phosphates, potash, shale oil
Land use: arable land: 3.32% permanent crops: 1.18% other: 95.5% (2005)
Irrigated land: 750 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: droughts; periodic earthquakes
Environment - current issues: limited natural fresh water resources; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: strategic location at the head of the Gulf of Aqaba and as the Arab country that shares the longest border with Israel and the occupied West Bank