The Geography of Djibouti
The Geography of Djibouti
Djiboutian Geography
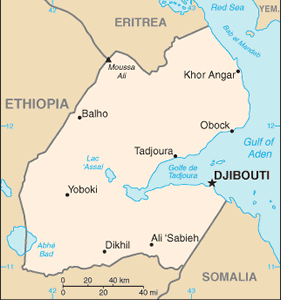
Location: Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, between Eritrea and Somalia
Geographic coordinates: 11 30 N, 43 00 E
Map references: Africa
Area: total: 23,000 sq km land: 22,980 sq km water: 20 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Massachusetts
Land boundaries: total: 516 km border countries: Eritrea 109 km, Ethiopia 349 km, Somalia 58 km
Coastline: 314 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm contiguous zone: 24 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: desert; torrid, dry
Terrain: coastal plain and plateau separated by central mountains
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Lac Assal -155 m highest point: Moussa Ali 2,028 m
Natural resources: geothermal areas, gold, clay, granite, limestone, marble, salt, diatomite, gypsum, pumice, petroleum
Land use: arable land: 0.04% permanent crops: 0% other: 99.96% (2005)
Irrigated land: 10 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: earthquakes; droughts; occasional cyclonic disturbances from the Indian Ocean bring heavy rains and flash floods
Environment - current issues: inadequate supplies of potable water; limited arable land; desertification; endangered species
Environment - international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: strategic location near world's busiest shipping lanes and close to Arabian oilfields; terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia; mostly wasteland; Lac Assal (Lake Assal) is the lowest point in Africa