The Geography of French Polynesia
The Geography of French Polynesia
French Polynesian Geography
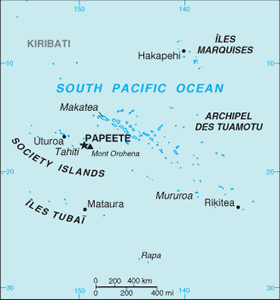
Location: Oceania, archipelagoes in the South Pacific Ocean about half way between South America and Australia
Geographic coordinates: 15 00 S, 140 00 W
Map references: Oceania
Area: total: 4,167 sq km (118 islands and atolls) land: 3,660 sq km water: 507 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly less than one-third the size of Connecticut
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 2,525 km
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate: tropical, but moderate
Terrain: mixture of rugged high islands and low islands with reefs
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m highest point: Mont Orohena 2,241 m
Natural resources: timber, fish, cobalt, hydropower
Land use: arable land: 0.75% permanent crops: 5.5% other: 93.75% (2005)
Irrigated land: 10 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: occasional cyclonic storms in January
Environment - current issues: NA
Environment - international agreements:
Geography - note: includes five archipelagoes (four volcanic, one coral); Makatea in French Polynesia is one of the three great phosphate rock islands in the Pacific Ocean - the others are Banaba (Ocean Island) in Kiribati and Nauru