The Geography of Malta
The Geography of Malta
Maltese Geography
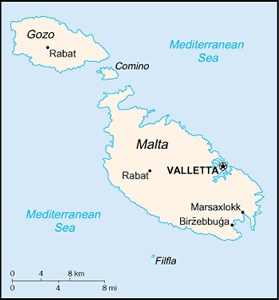
Location: Southern Europe, islands in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Sicily (Italy)
Geographic coordinates: 35 50 N, 14 35 E
Map references: Europe
Area: total: 316 sq km land: 316 sq km water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly less than twice the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 196.8 km (excludes 56.01 km for the island of Gozo)
Maritime claims: territorial sea: 12 nm contiguous zone: 24 nm continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation exclusive fishing zone: 25 nm
Climate: Mediterranean; mild, rainy winters; hot, dry summers
Terrain: mostly low, rocky, flat to dissected plains; many coastal cliffs
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m highest point: Ta'Dmejrek 253 m (near Dingli)
Natural resources: limestone, salt, arable land
Land use: arable land: 31.25% permanent crops: 3.13% other: 65.62% (2005)
Irrigated land: 20 sq km (2003)
Natural hazards: NA
Environment - current issues: limited natural fresh water resources; increasing reliance on desalination
Environment - international agreements: party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: the country comprises an archipelago, with only the three largest islands (Malta, Ghawdex or Gozo, and Kemmuna or Comino) being inhabited; numerous bays provide good harbors; Malta and Tunisia are discussing the commercial exploitation of the continental shelf between their countries, particularly for oil exploration